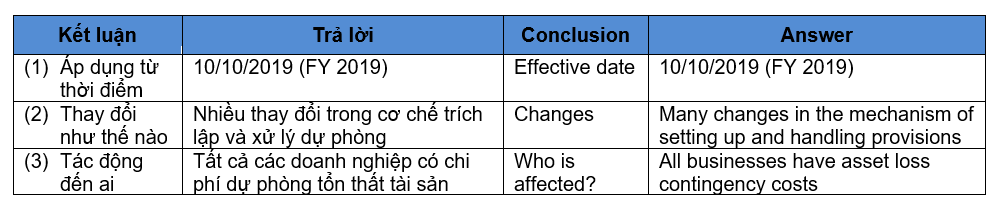
Giữa số liệu phản ánh trên báo cáo tài chính của doanh nghiệp (được lập và trình bày theo Luật và chuẩn mực kế toán) và số liệu báo cáo thuế (được lập và trình bày theo Luật thuế) luôn có sự khác biệt nhất định. Một trong các nội dung đó là việc hạch toán các khoản dự phòng tổn thất tài sản vào chi phí và việc chấp nhận chi phí này được trừ cho mục đích tính thuế thu nhập. Trong thực tế, do bản chất dự phòng là các khoản ước tính kế toán trong điều kiện không chắc chắn xảy ra, nhiều trường hợp doanh nghiệp gặp rủi ro do cơ quan thuế không chấp nhận chi phí này đáp ứng điều kiện là chi phí thực tế đã phát sinh tại doanh nghiệp
Ngày 8/8/2019, theo hướng dẫn mới nhất của Bộ Tài chính Việt Nam, việc trích lập dự phòng cho mục đích tính thuế thu nhập được thực hiện theo thông tư 48/2019/TT-BTC, thay thế hoàn toàn thông tư số 228/2009/TT-BTC và một số thông tư khác.
Rủi ro về chi phí dự phòng không hợp lệ bị loại khỏi chi phí được trừ

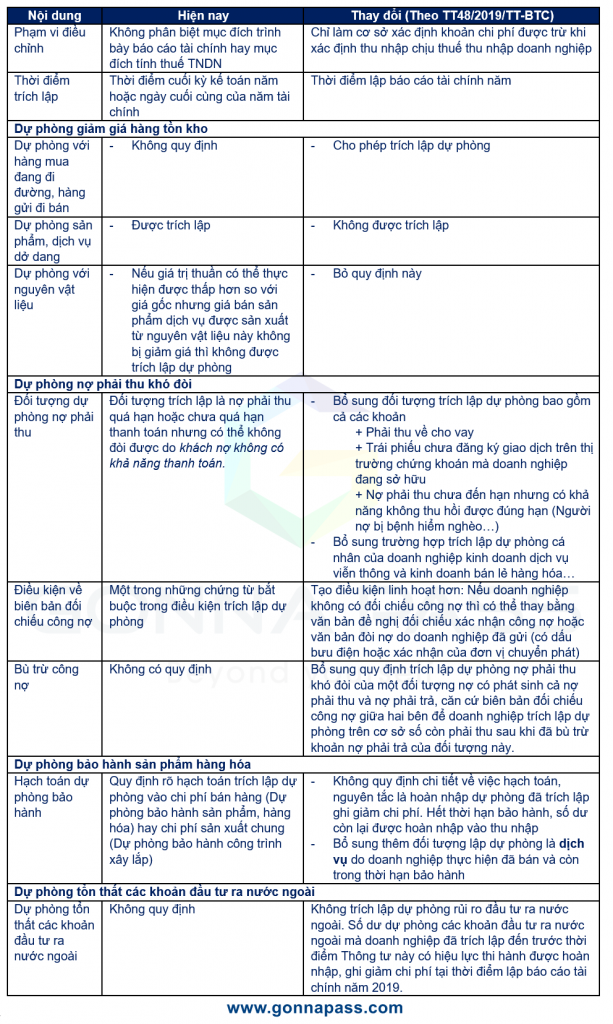
Một số điểm mới của thông tư 48/2019/TT-BTC bao gồm:
Căn cứ pháp lý:
Thông tư 48/2019/TT-BTC
There is a certain difference between the figures reflected in the financial statements (in accordance with accounting standards) and the figures of the tax report (in accordance with the Tax Law). One of such is the accounting of provision for loss of assets and whether the acceptance of this expense is deducted for the purpose of income tax calculation or not. In fact, due to the contingency nature of accounting estimates under uncertain conditions, there are many cases where a business is at risk because tax authorities do not accept this expense to meet the condition of deductible expenses.
On August 8, 2019, according to the latest guidance of the Ministry of Finance of Vietnam, the provision for income tax purposes is made in accordance with Circular 48/2019 / TT-BTC, completely replacing information. No. 228/2009 / TT-BTC and some other circulars. Some new points of this circular include
| Content | Now | Change |
| Scope of regulation | Irrespective of the purpose of presenting financial statements or CIT purposes | For determining deductible expenses when determining taxable income for corporate income tax |
| Time of setting up provision | At the end of the annual accounting period or the last day of the fiscal year | Time of making annual financial statements |
| Provision for devaluation of inventory
|
||
| Provision for goods in transit, goods sent for sale | – Not specified | – Eligible for a provision |
| Provision for WIP | – Eligible for a provision | – No provision |
| Provision for raw materials | – If net realizable value is lower than original cost, but the price of products and services manufactured from this material is not reduced, no provision is made | – Not specified |
| Provision for doubtful debts | ||
| Objects | Objects of setting up are receivable debts which are overdue or not yet overdue but cannot be reclaimed due to the solvency of debtors. | – Adding subjects to make provisions, including amounts
+ Receivables from loans + Bonds not registered for trading on stock market that enterprises currently own + Receivables that are not yet due but are not likely to be recovered on time (Debtors suffer from serious diseases …) – Supplementing the case of setting up personal provisions of telecommunication service enterprises and goods retailing enterprises… |
| Conditions on the debt reconciliation record | One of the mandatory documents in the provisioning conditions
|
More flexible conditions: If the enterprise does not have a debt reconciliation, it can be replaced by a written request for reconciliation. confirmation of debt or debt collection documents sent by the enterprise (postmarked or certified by the delivery unit) |
| Debt clearing | No provision | If a debtor has incurred both receivable and payable debts, based on the debt comparison record between the two parties, the enterprise shall make a provision on the basis of the receivable amount after clearing the liabilities |
| Provision for product warranty | ||
| Provision for product warranty | Specifying the accounting of the provisioning to selling expenses (provision for warranty of products and goods) or overhead costs (provision for warranty for construction works)
|
– There is no detailed regulation on accounting
– Adding the object of provision is a service performed by the enterprise and still in the warranty period |
| Provision for loss of offshore investments | ||
| Provision for loss of offshore investments | No provision | No provision for abroad investment. The balance of provision for offshore investments that enterprises have made up to before 10/10/2019 is reversed and recorded as cost reduction in 2019. |
Legal basis
Circular 48/2019/TT-BTC
Biên soạn: Nguyễn Việt Anh – Manager
Bản tin này chỉ mang tính chất tham khảo, không phải ý kiến tư vấn cụ thể cho bất kì trường hợp nào.
Để biết thêm thông tin cụ thể, xin vui lòng liên hệ với các chuyên viên tư vấn.
Đăng kí để nhận bản tin từ Gonnapass

